Free Access
Review
Table II.
Literature review of effective diffusion coefficients found for small solutes in different cheese types.
| Cheese | Composition dry matter (DM) (g·kg−1), fat/DM (g·100 g−1) and pH | Brining and/or ripening conditions |
Geometry | Model | Effective diffusion coefficient (D eff) (× 10−10 m2·s−1) | Refs. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process considered | Temperature (°C) | Brine composition | ||||||
| Solute: NaCl | ||||||||
| Camembert (soft-type cheese) | DM 410 fat/DM 45 | Brining and ripening | 14 | 300 g·kg−1 NaCl pH 4.6 | Slab | Fick (1D) | ~ 2.54 | [41] |
| Cuartirolo Argentino (soft-type cheese) | DM 480 fat/DM 51.7 | Brining and ripening | 7.5 | 205 g·kg−1 NaCl agitated or brine at rest | Finite rigid slab | Fick (1D) | 3.6 | [51, 52] |
| Feta | DM 440 fat/DM 43 | Dry-salted | 13 | – | Semi-finite geometry | Fick (1D) | 2.3 | [87] |
| White cheese (semi-hard, Turkey) | DM 450 fat/DM 42 pH 5.3 | Brining | 4, 12.5 and 20 | 150–200 g·kg−1 NaCl | Finite slab | Fick (1D) | 2.1, 3 and 4 (no effect of brine concentration) | [74] |
| White cheese (semi-hard, Turkey) | DM 450 fat/DM 42 pH 5.3 | Brining | 4–20 | 150–200 g·kg−1 NaCl | Finite slab | Fick (1D) | 2.2–4.2 | [75] |
| Prato cheese (semi-hard, Brazil) | DM 517 fat/DM 53 pH 5.2 | Brining | 10 | 150–200 and 250 g·kg−1 NaCl | Parallelepiped | Fick (3D) and neural network | 1.64, 4.25 and 3 | [7] |
| Romano (hard-type cheese) | DM 535 fat/DM 38 | Brining | 20 | 160 g·kg−1 NaCl | Slab | Fick (1D) | 2.54–3.35 | [35] |
| Sbrinz (hard-type cheese) | DM 650 fat/DM 48 | Brining and ripening | Brining at 12 °C (4 days) and diffusion at 7, 11, 15 and 20 °C | 200 g·kg−1 NaCl | Touching semi-infinite cylinders (after the brining step) | Fick (1D) | 1.06 (± 0.15) to 1.88 (± 0.27) (temp. coef.: 0.063 × 10−10 m2·s−1·°C−1) | [29] |
| Cheddar (hard-type cheese) | DM 650 | Ripening | 10 | – | Slab | Fick (1D) | 1.16 | [86] |
| Emmental (hard-type cheese) | DM 600 fat/DM 48 | Brining | 4–18 | 250 g·kg−1 NaCl; 0.3 g·kg−1 CaCl2 pH 5.4 | Infinite cylinder | Fick (1D) | 0.62–2.22 | [60] |
| Model cheese (Gouda style) | DM 580–630 fat/DM ~ 50 | Ripening RH 87% | 13 | – | Slab | Fick (1D) | 2.3 | [28] |
| Model cheese (Gouda style) | DM 533, 566 and 638 fat/DM 62, 50, 22 and 12 pH 4.9–5.6 | Brining | 12.6 | 130–310 g·kg−1 NaCl; 15 g·kg−1 CaCl2 | Flat cylindrical shape | Fick (1D) | ~ 2.3 1.16–3.24 (temp. coef.: 0.12 × 10−10 m2·s−1·°C−1) | [26] |
| Model cheese | DM 370 and 440 fat/DM 20 and 40 pH 6.2 and 6.5 0.5 and 1.5 g·100 g−1 NaCl | Release of NaCl from the cheese into water | 13 | Water | Infinite cylinder | Fick (1D) | 2.74–5.1 (± 0.01) | [46] |
| 15 | Artificial saliva | Fick (1D) | 2.81–3.43 | [23] | ||||
| Solute: water | ||||||||
| White cheese (semi-hard, Turkey) | DM 450 fat/DM 42 pH 5.3 | Brining | 4, 12.5 and 20 | 150–200 g·kg−1 NaCl | Finite slab | Fick (1D) | 15% brine: 1.96–3.64; 20% brine: 1.69–3.09 | [76] |
| Solutes: NaCl and water | ||||||||
| Fresh cheese Pasteurized cow and goat milk | No data | Brining | 5, 15 and 20 | 280 g·L−1 NaCl; 15 g·L−1 CaCl2 | Cylinder and parallelepiped | Fick (1D) | Water: 5.71, 8.83 and 9.99; NaCl: 3.56, 8.26 and 9.17 | [70] |
| Mahon cheese (soft-type cheese, Spain) | DM 244 | Ripening RH 85% | 12 | 280 g·L−1 NaCl; 15 g·L−1 CaCl2 | Parallelepiped | Fick (3D) | Water: 0.078; NaCl: 5.3 | [71] |
| Gouda (semi-hard cheese) | DM 565 fat/DM 53 | Brining | 20 | 170 g·kg−1 NaCl | Slab | Maxwell-Stefan (1D) |
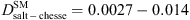 from the core to the edge of the cheese from the core to the edge of the cheese |
[61] |
| Solutes: NaCl and KCl | ||||||||
| Fynbo cheese (semi-hard, Turkey) | DM 470 fat/DM 29.6–36.2 | Brining | 12 | 100 g·L−1 NaCl; 100 g·L−1 KCl; 15 g·L−1 CaCl2 | Diffusion cell | Fick (1D) | NaCl: 4.14; KCl: 3.91 | [89] |
| Prato cheese (semi-hard, Brazil) | DM 540 fat/DM 52.8 | Brining | 10 | 146 g·L−1 NaCl; 50.6 g·L−1 KCl; 5 g·L−1 CaCl2 | Parallelepiped | Fick (1D) | NaCl: 2.6; KCl: 2.77 | [8] |
| Prato cheese (semi-hard, Brazil) | DM 540 fat/DM 52.8 | Brining | 10 | 146 g·L−1 NaCl; 50.6 g·L−1 KCl; 5 g·L−1 CaCl2 | Parallelepiped | Fick (3D) | NaCl: 2.8; KCl: 2.94 | [10] |
| Other solutes | ||||||||
| Lactose in small curd cottage cheese | No available information | Washing | 25 | Demineralized water pH 4.5 (H3PO4) | Sphere | Fick (1D) | 3.8 | [11] |
| Lactose in Skimmed Quark cheese (Soft-type cheese, Germany) | No available information | – | 4 | – | Touching semi-infinite cylinders | Fick (1D) | 1.37 (± 0.13) | [85] |
| Sucrose in milk | Fat 15 g·kg−1 | Contact with 15 g·100 g−1 agar gel | 20–24 (room temperature) | – | Touching semi-infinite cylinders | Fick (1D) | Initial gel sucrose concentration C s0 787 g·L−1: 1.9, C s0 515 g·L−1: 2.6, C s0 279 g·L−1: 3.9 | [81] |
| Lactic acid and NaCl in Pategras | DM 544 fat/DM 43 Lactic acid 13 g·kg−1 | Ripening RH 90% | 13 | 200 g·kg−1 NaCl; 5 g·kg−1 CaCl2 | Finite slab | Fick (1D) multicomponent diffusion | NaCl: 3.2 lactic acid: ~ 1 | [25] |
| Potassium sorbate in American processed cheese | DM 600 fat/DM 45 | Brining | Room temperature | 250 g·L−1 potassium sorbate solutions | Cubes (finite slab) | Fick (1D) | 1.31 | [40] |
| Potassium sorbate in Mozzarella | DM ~ 500 fat/DM 45 | 0.674 | ||||||
| Aroma compounds in model cheese: diacetyl, heptan-2-one, and ethyl hexanoate | DM 370 fat/DM 20 and 40 pH 6.2 1.5 g·100 g−1 NaCl | Release of aroma compounds in the air | 13 | – | VASK | Fick (1D) | Diacetyl: 0.04; heptan-2-one: 0.2–0.12; ethyl hexanoate: 0.18–0.07 | [47] |


